🌟 Introduction
The food industry is undergoing a massive digital transformation. With rising consumer expectations, supply chain disruptions, climate variability, and food safety challenges, organizations increasingly rely on Food Analytics to make smarter, faster, and safer decisions.
Food Analytics integrates data science, AI, IoT, and statistical modeling to improve production, quality, supply chains, pricing, nutrition, sustainability, and safety across the entire food ecosystem — from farm to fork.
In this article, we’ll explore what Food Analytics is, key techniques, real-world applications, and examples backed by well-known industry practices.
🍏 What Is Food Analytics?
Food Analytics refers to the analysis of food-related data to optimize decision-making in production, processing, distribution, safety, and consumption.
It combines:
- Data analytics
- AI & machine learning
- Chemical & nutritional analysis
- Supply chain analytics
- Consumer behavior insights
- Digital sensors & IoT systems
Food analytics helps companies answer critical questions:
- How do we ensure consistent quality?
- How can we reduce waste?
- What products should we produce next season?
- Is the food safe for consumption?
- How do we optimize transportation and pricing?
🌱 Key Domains of Food Analytics
1️⃣ Production Analytics (Farm-level Data)
Food production is increasingly data-driven. Sensors, drones, and GIS systems provide real-time data on soil, weather, pests, irrigation, and crop growth.
Examples
- Predicting crop yield using machine learning
- Optimizing fertilizer and water usage
- Detecting early pest or disease outbreaks
- Forecasting harvest windows
📌 Real World: John Deere uses IoT-enabled tractors and AI to recommend optimal planting patterns.
2️⃣ Quality Analytics (Chemical & Sensory Profiles)
Ensuring food quality involves analyzing:
- Nutritional content
- Moisture, pH
- Texture, color, aroma profiles
- Shelf-life predictions
Examples
- Using spectroscopy to detect adulteration in milk and oils
- Modeling spoilage rates under different storage conditions
- Sensory scoring systems (e.g., coffee cupping, wine profiles)
📌 Real World: Nestlé employs near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy to test ingredient quality instantly.
3️⃣ Food Safety Analytics
Food safety requires constant monitoring of contamination risks through microbiological, chemical, and environmental data.
Examples
- AI models predicting Salmonella risk in poultry
- IoT sensors monitoring cold chain temperature violations
- Hazard Analysis (HACCP) dashboards highlighting risk zones
📌 Real World: Walmart uses blockchain-based traceability to identify contamination sources within seconds.
4️⃣ Supply Chain & Logistics Analytics
Food supply chains are vulnerable to spoilage, delays, weather disruptions, and demand unpredictability.
Analytics helps optimize:
- Inventory
- Routing
- Cold chain management
- Vendor performance
- Procurement
Examples
- Predicting demand for perishable goods using time-series forecasting
- Route optimization algorithms minimizing fuel & spoilage
- Using RFID tags to monitor temperature in cold chain trucks
📌 Real World: Amazon Fresh uses predictive models for fresh produce replenishment.
5️⃣ Consumer Analytics & Personalization
Consumer preferences shape food trends. Companies analyze:
- Purchase behavior
- Dietary patterns
- Social media sentiment
- Nutritional choices
Examples
- Recommending personalized diet plans using AI
- Market basket analysis for cross-selling (e.g., yogurt + granola)
- Menu optimization using sales and waste data
📌 Real World: Starbucks uses loyalty data and ML to personalize food recommendations.
6️⃣ Sustainability & Waste Reduction Analytics
Food waste is a global challenge — nearly 1/3 of all food is lost or wasted.
Analytics helps organizations:
- Forecast demand accurately
- Monitor shelf-life
- Optimize storage conditions
- Reduce carbon footprint
Examples
- Machine learning predicting the remaining freshness of fruits
- Optimizing packaging materials to extend shelf life
- Using LCA (Life Cycle Assessment) for sustainable sourcing
📌 Real World: Too Good To Go app analyzes surplus food patterns to reduce retail waste.
🧮 Analytics Techniques Used in Food Analytics
| Technique | Application |
|---|---|
| Machine Learning | Yield prediction, spoilage detection, price forecasting |
| Image Processing | Food classification, defect detection |
| Spectroscopic Analytics | Nutrient, moisture, adulteration analysis |
| Time-series Forecasting | Demand and inventory prediction |
| Optimization Models | Transportation, production planning |
| Blockchain Analytics | Traceability & transparency |
| IoT Sensor Analytics | Cold-chain monitoring, cooking optimization |
👨🍳 Example Problem: Predicting Food Spoilage
A dairy company collects temperature data of milk transported over 8 hours. The spoilage rate increases if temperature exceeds 4°C.
Using logistic regression, they model:
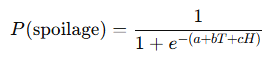
Where:
- T = temperature
- H = hours exposed above 4°C
By analyzing historical spoilage data, they identify:
- If T > 6°C for more than 40 minutes, spoilage probability exceeds 80%.
Outcome: They set new operational thresholds for refrigeration units in trucks.
🥗 Example Problem: Menu Profit Optimization
A restaurant analyzes:
- ingredient cost
- preparation time
- historical sales
- customer ratings
Using linear programming, they determine which dishes maximize profit under constraints like staff capacity and cooking time.
📈 Real-World Applications by Sector
| Sector | Food Analytics Use Case |
|---|---|
| Dairy | Adulteration detection, cold-chain analytics |
| Beverages | Flavor modeling, fermentation optimization |
| Bakery | Texture profiling, shelf-life estimation |
| Meat & Poultry | Microbial risk prediction |
| Fruits & Vegetables | Ripeness detection via computer vision |
| Retail | Dynamic pricing for perishable goods |
🔮 Future of Food Analytics
The next evolution includes:
- AI-powered recipe generation
- Precision fermentation analytics
- Real-time blockchain-enabled traceability
- Robotics in food sorting & grading
- Nutrigenomics-driven diet personalization
Food analytics will enable safer, healthier, and more sustainable food systems.
📚 References
- Applications of artificial intelligence (AI) in managing food quality and ensuring global food security (2024). CyTA. Journal of Food, 22(1).
- FAO. (2020). Global Food Loss and Waste Report.
- McKinsey. (2023). Digitization in Agriculture and Food Supply Chains.
- Nestlé R&D Publications – Spectroscopic Testing Methods.
- IBM Food Trust – Blockchain in Food Traceability.
- Too Good To Go. (2023). Impact Report.
- Artificial Intelligence and IOT Approaches for Enhancing Precision Agricultural Machinery (2023).








Leave a comment