🌟 Introduction
In the era of data-driven decision-making, every click, transaction, and sensor reading generates massive amounts of data. But this data has little value unless it’s collected, stored, managed, and processed efficiently — and that’s exactly what Data Systems are designed to do.
From the apps on your phone to the cloud services powering global enterprises, data systems are the invisible engines that keep the digital ecosystem running.
In this article, we’ll explore what data systems are, their types, components, architecture, and real-world examples — and why they’re vital for analytics and AI.
🔍 What are Data Systems?
A Data System is a structured framework of hardware, software, and processes that collect, store, process, and deliver data efficiently and securely for various applications.
In simple terms:
A data system is an ecosystem that handles data throughout its life cycle — from creation to consumption.
It enables businesses to move from raw data to actionable insights.
🧮 Components of a Data System
A typical data system consists of five core components:
| Component | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Data Sources | Where data originates | Sensors, transactions, social media, IoT devices |
| Data Ingestion | Collecting and importing data into storage | APIs, ETL tools, Kafka streams |
| Data Storage | Persisting data in structured or unstructured form | Databases, Data Lakes, Warehouses |
| Data Processing | Transforming raw data into useful formats | Hadoop, Spark, ETL pipelines |
| Data Access / Analytics Layer | Interface for users and applications | SQL, BI tools, APIs |
Flow diagram showing Components of a Data System

🧱 Types of Data Systems
Data systems come in various forms, depending on the type and purpose of the data they handle.
1️⃣ Transactional Data Systems (OLTP)
- Designed for handling real-time transactions — such as purchases, payments, or bookings.
- Focused on speed, accuracy, and reliability.
- Data is normalized to avoid duplication.
Examples:
- Banking systems processing ATM withdrawals.
- E-commerce checkout systems (e.g., Amazon’s order database).
- Railway or airline booking systems.
Technologies: MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server.
Snapshot of a real-time order transaction flow:
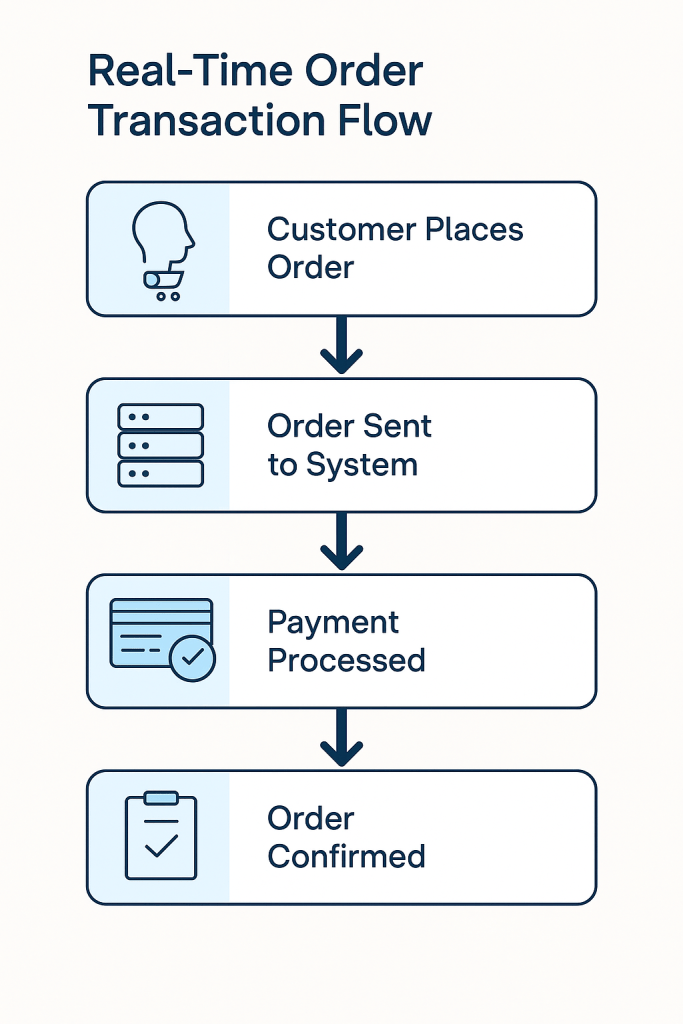
2️⃣ Analytical Data Systems (OLAP)
- Used for analysis and reporting, not transactions.
- Optimized for read-heavy workloads (e.g., generating summaries and dashboards).
- Data is aggregated and denormalized for performance.
Examples:
- Business Intelligence dashboards (Power BI, Tableau).
- Sales performance analysis.
- Predictive modeling systems.
Technologies: Snowflake, Amazon Redshift, Google BigQuery, Apache Druid.
🧠 Analogy: OLTP = daily transactions; OLAP = monthly reports.
3️⃣ Data Warehouses
- Centralized repositories that store structured, historical data from multiple sources.
- Support analytics, reporting, and trend analysis.
- Enable a “single source of truth” for enterprises.
Examples:
- Enterprise Data Warehouse (EDW) for retail sales data.
- Healthcare warehouse integrating hospital and lab data.
Technologies: Snowflake, Amazon Redshift, Google BigQuery, Azure Synapse.
4️⃣ Data Lakes
- Store raw, unstructured, or semi-structured data — logs, images, IoT sensor data.
- Enable big data processing and machine learning use cases.
- Highly scalable and flexible.
Examples:
- Storing raw IoT sensor data before analysis.
- Collecting web logs or social media streams.
Technologies: Hadoop, AWS S3, Azure Data Lake, Google Cloud Storage.
Comparison of Warehouse vs. Data Lake vs. Lakehouse
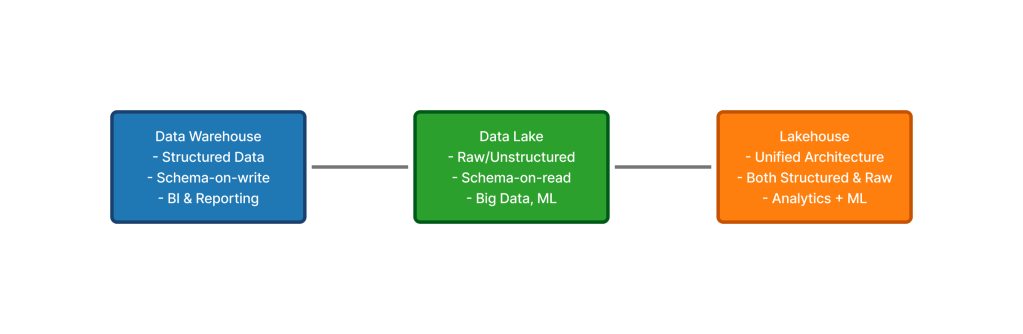
5️⃣ Data Lakehouse (Modern Hybrid Systems)
A data lakehouse combines the best of both worlds:
- The flexibility of a data lake,
- The performance and structure of a data warehouse.
Example Technologies: Databricks Lakehouse, Snowflake Unistore, Delta Lake.
✅ Supports real-time analytics, AI, and machine learning workflows.
6️⃣ Real-time Streaming Systems
- Handle continuous data streams from live sources.
- Used in systems that require immediate response.
Examples:
- Fraud detection in banking.
- Live monitoring in logistics or energy grids.
- Stock price analytics.
Technologies: Apache Kafka, Apache Flink, AWS Kinesis, Spark Streaming.
🧠 Example Use Case: End-to-End Data System
Scenario: Smart Farming Analytics Platform
| Stage | Example Implementation |
|---|---|
| Data Source | IoT sensors in the field (temperature, humidity, soil moisture) |
| Ingestion | Apache Kafka streams data in real-time |
| Storage | AWS S3 for raw data; PostgreSQL for structured records |
| Processing | Apache Spark cleans and aggregates data |
| Analytics Layer | Power BI dashboard shows crop health trends |
| Prescriptive Action | AI model recommends irrigation schedule |
🧩 Outcome: Improved yield prediction and resource optimization.
⚙️ Data System Architecture
Key Layers in a Modern Data System:
- Data Ingestion Layer: Connects sources and pipelines.
- Storage Layer: Manages structured/unstructured data.
- Processing Layer: Cleans, transforms, and aggregates.
- Analytics Layer: Provides dashboards and visual insights.
- Governance & Security Layer: Ensures data quality, compliance, and access control.
📊 Real-World Examples
| Organization | Type of Data System | Purpose / Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Netflix | Real-time Data Lakehouse | Personalized recommendations |
| Amazon | Data Warehouse + OLTP | Inventory, pricing, recommendation engine |
| Uber | Streaming Data System | Live driver-passenger matching |
| Starbucks | Analytics Warehouse | Predicting customer purchase behavior |
| NASA | Big Data Systems | Satellite image analysis and space research |
🔒 Importance of Data Governance in Data Systems
A good data system isn’t just about speed or storage — it must also ensure:
- Data Quality: Accuracy and completeness.
- Data Security: Controlled access and encryption.
- Compliance: GDPR, HIPAA, or data privacy laws.
- Metadata Management: Understanding where data comes from and how it’s used.
🧠 Pro tip: Always design data systems with governance-first architecture.
🧾 Key Takeaways
✅ Data systems are the backbone of digital transformation.
✅ They manage data across the full lifecycle — from source to insight.
✅ The modern trend is toward integrated, cloud-based, and real-time architectures.
✅ Choosing the right data system depends on your use case, scale, and performance needs.
📚 Further Reading
- Martin Kleppmann, Designing Data-Intensive Applications, O’Reilly Media.
- James Serra, Modern Data Architecture: The Data Lakehouse Concept.
- Gartner (2023). The Evolution of Data Management Systems.
- Google Cloud: Modern Data Systems Overview
- Databricks Blog: Data Lakehouse Architecture Explained









Leave a comment