🌟 Introduction
In business, supply chains, finance, manufacturing, agriculture, transport, and even daily planning, we constantly face situations where resources are limited. Linear Programming (LP) is one of the most powerful mathematical tools to allocate scarce resources optimally.
From choosing the best product mix, minimizing transportation costs, or optimizing crop planning, LP turns complex decisions into solvable mathematical models.
🔍 What is Linear Programming?
Linear Programming (LP) is a mathematical optimization technique used to determine the best possible outcome under a set of linear constraints.
In simple terms:
Linear Programming helps you maximize profit or minimize cost while satisfying certain resource limitations.
🎯 Components of a Linear Programming Model
Any LP model consists of four key components:
1️⃣ Decision Variables
These represent the choices to be made.
Example:

2️⃣ Objective Function
This is what you want to maximize (profit) or minimize (cost).
Example:
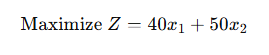
3️⃣ Constraints
These represent the resource limitations.
Examples:
- Machine hours
- Budget limits
- Labor
- Raw materials
These constraints must be linear, e.g.,
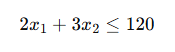
4️⃣ Non-negativity Constraints
Since negative production is impossible:
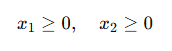
🧱 Mathematical Structure of an LP Model
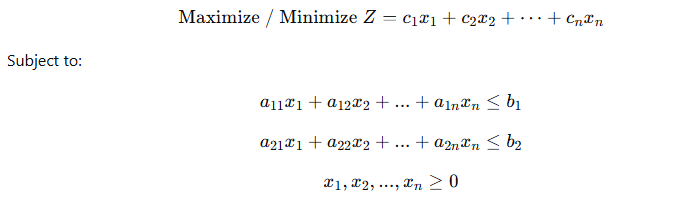
🧮 Solved Example 1: Product Mix Optimization (Graphical Method)
A company produces two products, A and B.
| Resource | Product A | Product B | Availability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Machine Hours | 2 | 3 | 120 |
| Labor Hours | 3 | 2 | 100 |
Profit:
- Product A: ₹40
- Product B: ₹50
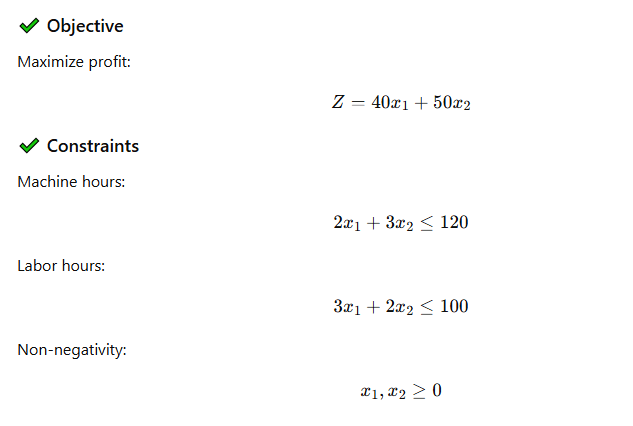
Step 1: Convert constraints to lines
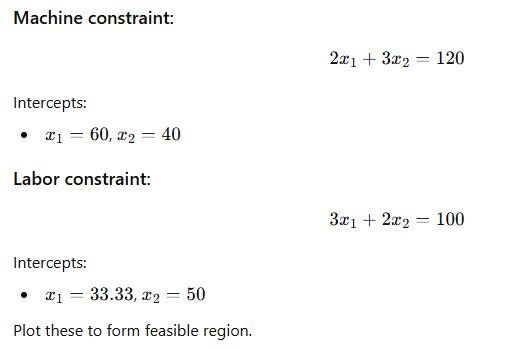

Step 2: Identify corner points
The feasible region corner points are:
- (0, 0)
- (0, 40)
- Intersection of both constraints
- (33.33, 0)
Step 3: Solve intersection point
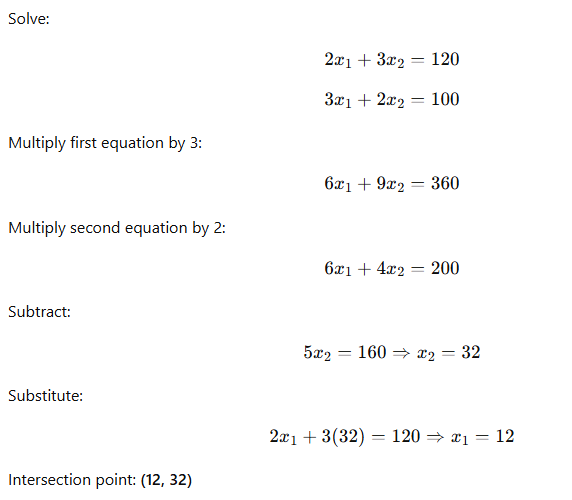
Step 4: Evaluate objective function
| Point | Profit Z |
|---|---|
| (0, 0) | 0 |
| (0, 40) | 2000 |
| (33.33, 0) | 1333.2 |
| (12, 32) | 40×12 + 50×32 = 800 + 1600 = 2400 |
⭐ Optimal Solution
Produce:
- 12 units of A
- 32 units of B
Maximum Profit = ₹2400
🧮 Solved Example 2: Diet Optimization Problem
A person wants to meet nutritional needs at minimum cost.
Food A and B provide nutrients as:
| Nutrient | Food A | Food B | Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protein | 4 | 2 | ≥ 12 |
| Carbs | 2 | 4 | ≥ 12 |
| Cost | ₹6 | ₹8 | Minimize |
✔ Decision variables
x = units of Food A
y = units of Food B

Solve intersections
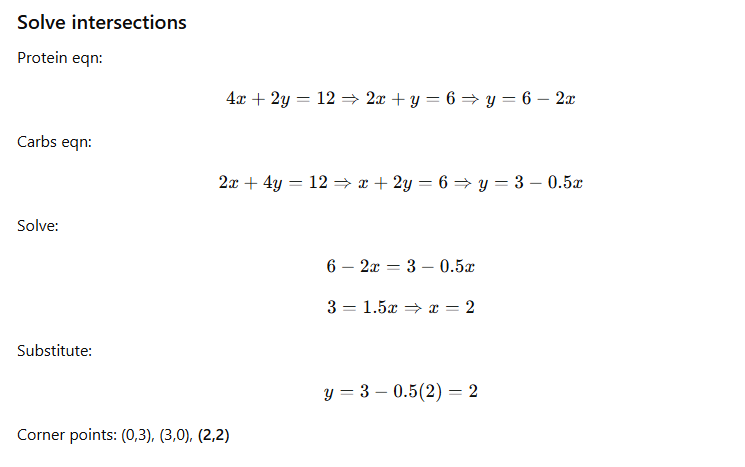
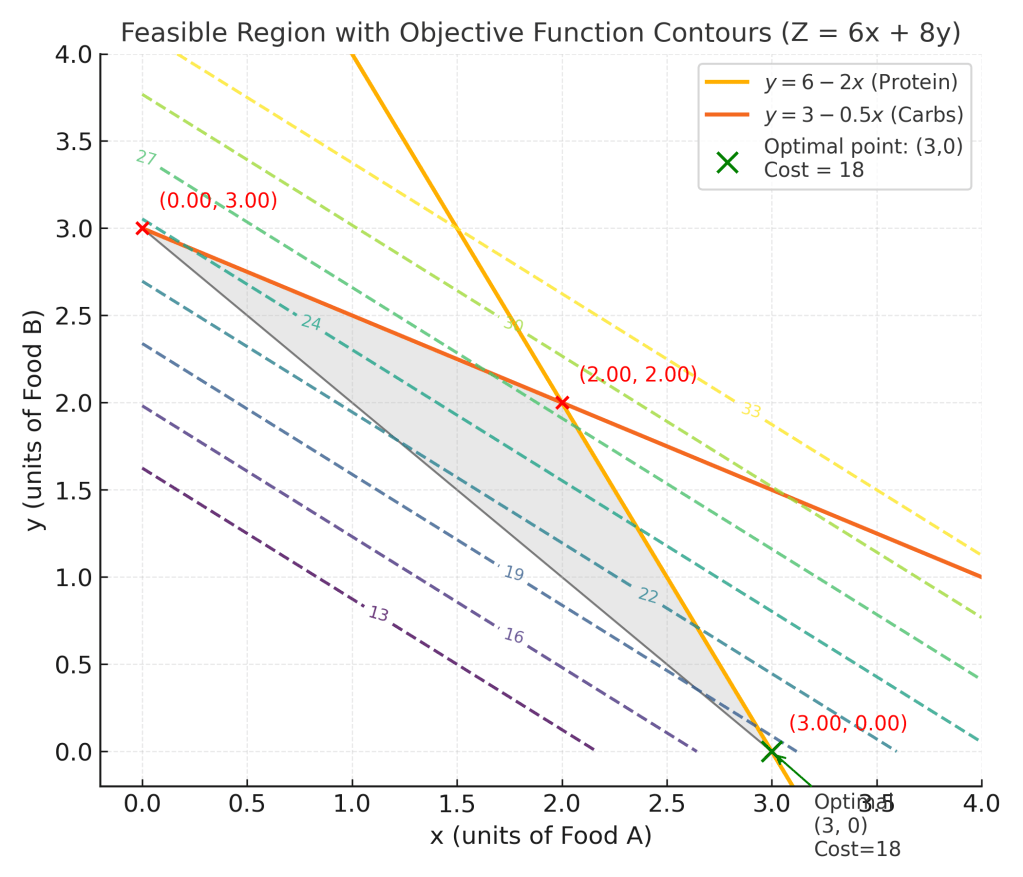
Evaluate cost:
- (3,0): 6×3 = 18
- (0,3): 8×3 = 24
- (2,2): 6×2 + 8×2 = 28
Minimum is actually 18 at (3,0).
⭐ Optimal Solution
Eat:
- 3 units of Food A
- 0 units of Food B
Minimum cost = ₹18
📊 Applications of Linear Programming
| Industry | LP Application |
|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Product mix, job scheduling |
| Logistics | Transportation & routing |
| Agriculture | Crop planning, fertilizer allocation |
| Energy | Grid optimization |
| Finance | Portfolio optimization |
| Marketing | Budget allocation |
| Healthcare | Staff scheduling, resource planning |
🔧 Solving LP in Python (PuLP)

🧾 Final Takeaways
✔ LP is one of the most widely used optimization tools.
✔ Helps allocate limited resources optimally.
✔ Works best when relationships are linear.
✔ Solvable using both graphical method (2 variables) and Simplex Method (many variables).
📚 Further Reading
- Fred Hillier & Gerald Lieberman – Introduction to Operations Research
- Bazaraa, Jarvis & Sherali – Linear Programming and Network Flows
- Winston – Operations Research: Applications and Algorithms









Leave a comment