🌟 Introduction
Machine Learning (ML) has become a core component of modern analytics, powering applications such as demand forecasting, fraud detection, medical diagnosis, recommendation systems, and image recognition.
At a high level, supervised machine learning models are broadly classified into:
- Regression Models – used when the output is continuous
- Classification Models – used when the output is categorical
Understanding the difference between these two, their algorithms, and use cases is fundamental for anyone working in analytics, data science, or AI.
🔍 Supervised Learning in Brief
In supervised learning, models are trained using labeled data, where both:
- Input features (X) and
- Output variable (Y)
are known.
The model learns a mapping:
Y = f(X)
Depending on the nature of Y, the problem becomes either regression or classification.
📈 Regression Models
📌 What is Regression?
Regression models predict a continuous numerical value.
Examples of regression problems:
- Predicting house prices
- Forecasting sales revenue
- Estimating crop yield
- Predicting temperature or rainfall
- Predicting time to failure of a machine
🧮 Common Regression Algorithms
1️⃣ Linear Regression
Concept
Linear Regression models the relationship between input variables and a continuous output using a straight line.
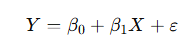
Example
Predicting house price based on size:
- X = house size (sq. ft.)
- Y = house price (₹)
If:
Y = 50000 + 3000X
Then a 1000 sq. ft. house price:
Y = 50000 + 3000(1000) = ₹30,50,000
📌 Use cases: real estate, cost estimation, trend analysis.
2️⃣ Multiple Linear Regression
Uses multiple predictors:
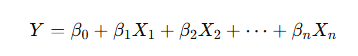
Example:
Predicting crop yield using:
- rainfall
- fertilizer usage
- temperature
3️⃣ Polynomial Regression
Models non-linear relationships by adding polynomial terms.
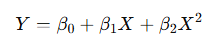
📌 Used when the relationship curves rather than being linear.
4️⃣ Regularized Regression
Used to prevent overfitting.
| Model | Key Idea | Use |
|---|---|---|
| Ridge | Penalizes large coefficients (L2) | Multicollinearity |
| Lasso | Performs feature selection (L1) | Sparse models |
| Elastic Net | Combines L1 + L2 | High-dimensional data |
5️⃣ Tree-Based Regression Models
- Decision Tree Regressor
- Random Forest Regressor
- Gradient Boosting / XGBoost
📌 Widely used for complex, non-linear relationships.
📊 Regression Evaluation Metrics
| Metric | Meaning |
|---|---|
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
| MSE / RMSE | Penalizes large errors |
| R² | Variance explained by model |
🧠 Classification Models
📌 What is Classification?
Classification models predict categorical outcomes (labels or classes).
Examples:
- Spam vs Not Spam
- Fraud vs Legitimate
- Disease: Yes / No
- Customer churn: Yes / No
- Product category prediction
🧮 Common Classification Algorithms
1️⃣ Logistic Regression
Despite its name, Logistic Regression is a classification model.
Concept
It predicts the probability of a class using a sigmoid function.

Example
Predicting whether a customer will churn:
- Output: 1 = churn, 0 = no churn
- If probability > 0.5 → classify as churn
📌 Used in credit scoring, medical diagnosis, marketing.
2️⃣ Decision Tree Classifier
- Uses if–else rules
- Easy to interpret
- Can overfit without pruning
Example:
Loan approval based on:
- income
- credit score
- employment status
3️⃣ Random Forest Classifier
- Ensemble of decision trees
- Reduces overfitting
- High accuracy
📌 Widely used in fraud detection and risk modeling.
4️⃣ Support Vector Machine (SVM)
- Finds an optimal decision boundary (hyperplane)
- Effective in high-dimensional spaces
📌 Used in text classification and bioinformatics.
5️⃣ k-Nearest Neighbors (k-NN)
- Classifies based on majority vote of neighbors
- Simple but computationally expensive
6️⃣ Naïve Bayes Classifier
- Based on Bayes’ theorem
- Assumes feature independence
📌 Popular in spam filtering and sentiment analysis.
7️⃣ Neural Networks
- Multi-layer perceptrons (MLP)
- Used in image, speech, and NLP tasks
📊 Classification Evaluation Metrics
| Metric | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Accuracy | Overall correctness |
| Precision | Correct positive predictions |
| Recall (Sensitivity) | Ability to detect positives |
| F1-score | Balance of precision & recall |
| ROC–AUC | Model discrimination ability |
🔁 Regression vs Classification: Key Differences
| Aspect | Regression | Classification |
|---|---|---|
| Output | Continuous | Categorical |
| Example | Predict sales | Predict churn |
| Algorithms | Linear, Ridge, RF | Logistic, SVM, RF |
| Metrics | RMSE, R² | Accuracy, F1, AUC |
🧩 End-to-End Example
Problem: Predict customer behavior
- Step 1: Use regression to predict customer lifetime value (CLV)
- Step 2: Use classification to predict churn risk
- Step 3: Combine insights for targeted marketing
This hybrid approach is common in business analytics.
🌍 Real-World Applications
| Industry | Regression Use | Classification Use |
|---|---|---|
| Finance | Stock price prediction | Fraud detection |
| Healthcare | Length of stay | Disease diagnosis |
| Retail | Demand forecasting | Customer segmentation |
| Agriculture | Yield estimation | Crop disease detection |
| Manufacturing | Failure time prediction | Defect classification |
🧪 Simple Python Illustration
# Regression
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
# Classification
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
clf = LogisticRegression()
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = clf.predict(X_test)
⚠️ Common Pitfalls
- Using regression when output is categorical
- Ignoring class imbalance in classification
- Overfitting complex models
- Not validating model assumptions
🧾 Key Takeaways
✔ Regression predicts how much
✔ Classification predicts which class
✔ Model choice depends on data, problem, and business goal
✔ Evaluation metrics differ significantly
📚 References & Further Reading
- Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R., & Friedman, J. (2017). The Elements of Statistical Learning. Springer.
- James, G., et al. (2021). An Introduction to Statistical Learning. Springer.
- Géron, A. (2022). Hands-On Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn, Keras & TensorFlow. O’Reilly.
- Bishop, C. (2006). Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning. Springer.
- scikit-learn documentation: https://scikit-learn.org
- Kaggle Learn: Regression & Classification Micro-courses









Leave a comment